The musculoskeletal system is the most important part of our body. You often need to see a doctor because of your back pain.
Regular back pain, stiffness in movements and muscle cramps are caused by osteochondrosis of the back - a disease of the bone and cartilage tissues and the musculoskeletal system caused by various factors affecting the body.
Back osteochondrosis is a problem caused by many.
Etiology and pathogenesis of osteochondrosis
Posterior osteochondrosis manifests itself gradually, affecting all new zones of the spine in a latent form. Initially, changes occur in the structure of the discs of the vertebrae: they lose their elasticity, the space between the vertebrae decreases, and the nerve endings in the spinal cord are damaged.
The patient experiences back pain. Subsequently, the changes precede the smaller elements of the vertebral structure, degenerative growth of bone tissue develops that impede spinal mobility, healthy cartilage cells are destroyed, and the disease affects the bones and ligaments. As a side effect, deformity of the vertebrae causes an increase in the load on the organs and arteries. This is due to the peculiarity of the blood supply - the displacement of the segments of the spine causes compression of the vertebral artery and eventually a disruption of the severe blood circulation in the central nervous system.
The main problem that causes violation of spinal formation and the process of osteochondrosis is a lack of nutrition and a decrease in the blood supply to the tissues of the bone structure. The cause of development is a number of factors in a person’s external, internal influence and behavioral process.
The endogenous (internal) causes are:
- genetic factors of inheritance;
- violation of the metabolism of trace elements (phosphorus and calcium);
- cartilage tissue characteristics;
- age-related changes in the organization;
- overweight;
- orthopedic diseases.
Due to exogenous (external) causes and lifestyle, osteochondrosis is caused by:
- low level of physical development of the back muscles;
- spinal injuries;
- improper posture, scoliosis;
- systematic incorrect or uncomfortable posture;
- unbalanced diet, consumption of fatty fast foods;
- uneven physical exertion, rear overload;
- bad habits;
- constant stress.
The latent form of osteochondrosis can manifest itself by sharp lifting, jumping, and falling weights, which causes microtrauma of the spinal disc and damage to the nerve root.
This is when the patient may experience sharp shooting pain for the first time. In the future, the pain syndrome will return again and again with varying intensities. The nerve stem cells involved indicate the need for urgent medical intervention.
Classification of the disease, main stages
In medicine, osteochondrosis is classified according to the affected area of the spine:
- cervical;
- chest;
- lumbar and sacral region.
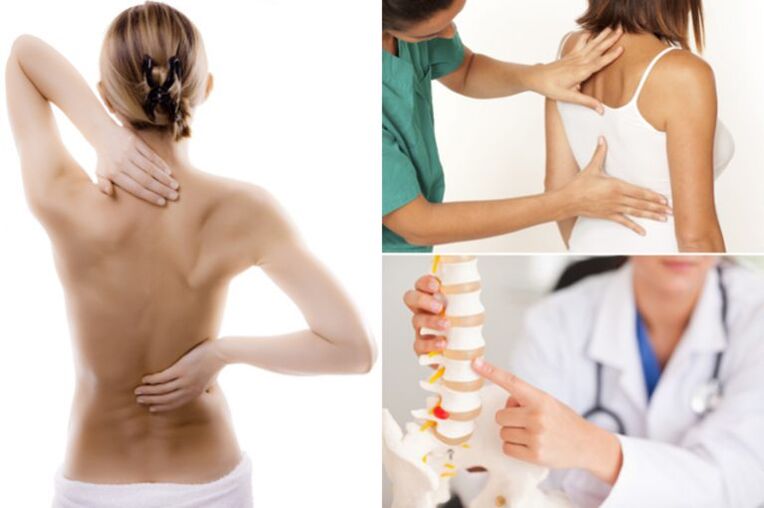
Osteochondrosis of the back is classified depending on the area affected.
The main stages of the development of the disease:
- The onset of osteochondrosis - microcracks are formed in the annulus fibrosus, moisture is lost from the bone and cartilage tissue. Stage manifests as subtle discomfort in one zone of the spine after physical exertion or uncomfortable position of the body.
- The first painful attacks make you feel. In the second stage, the plates protrude, the space between the discs decreases, and the fibrous capsule collapses, and the nerve roots become pinched. Pain indicates the process of metabolic disorders in cartilage tissue and its destruction. Ignoring the second stage of osteochondrosis gives a boost to cartilage inflammation and consequently damage to nerve fibers, blood, and lymphatics.
- In the third stage of the disease, the affected vertebrae are deformed and the cartilage tissue is cleared. With proper active treatment, further destruction of cartilage cells and curvature of the spine can be stopped. But in the future, supportive therapy and care will become the patient’s constant companion for normal physical activity.
- Onset osteochondrosis, which has entered the last fourth stage of development, often becomes the cause of the disability. All destructive processes are irreversible: significant displacement of the structure of the vertebrae, compaction of cartilage tissue, abnormal growth of bone tissue. With each movement, the patient experiences intense, sometimes unbearable pain.
Symptoms
Signs of joint osteochondrosis are easy to confuse with diseases similar to other symptoms. In addition, the manifestation symptoms of a separate sector of the vertebral structure have characteristic features.
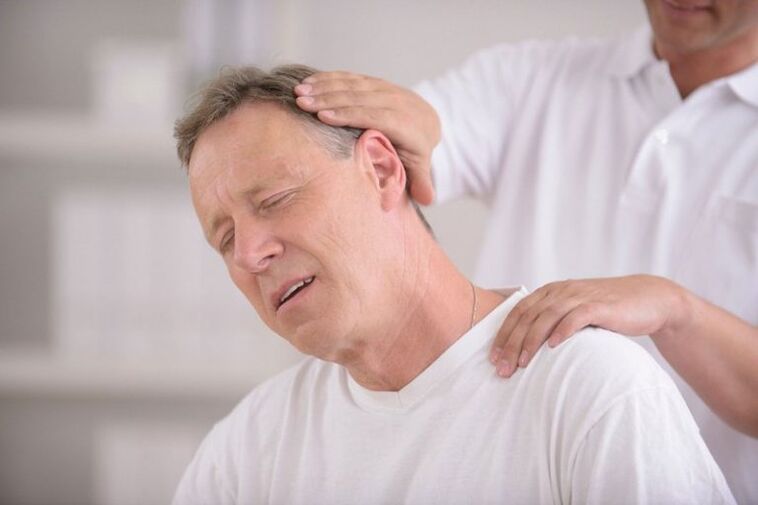
The main symptoms of osteochondrosis are:
- stiffness while moving, crackling, crackling, or difficulty;
- pain in the area of localization of inflammation (neck, chest or lumbar), of varying intensity and nature;
- numbness of the limbs;
- muscle weakness, decreased performance;
- pain attacks that radiate along nerve channels to related parts of the body (shoulders, shoulder blades, legs).
Cervical osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the cervix is expressed in the following diseases:
- pain in the neck or back of the head;
- dizziness;
- tinnitus, hearing and vision problems;
- slowness of the neck after sleep or the same posture for a long time;
- painful feelings when turning the head.
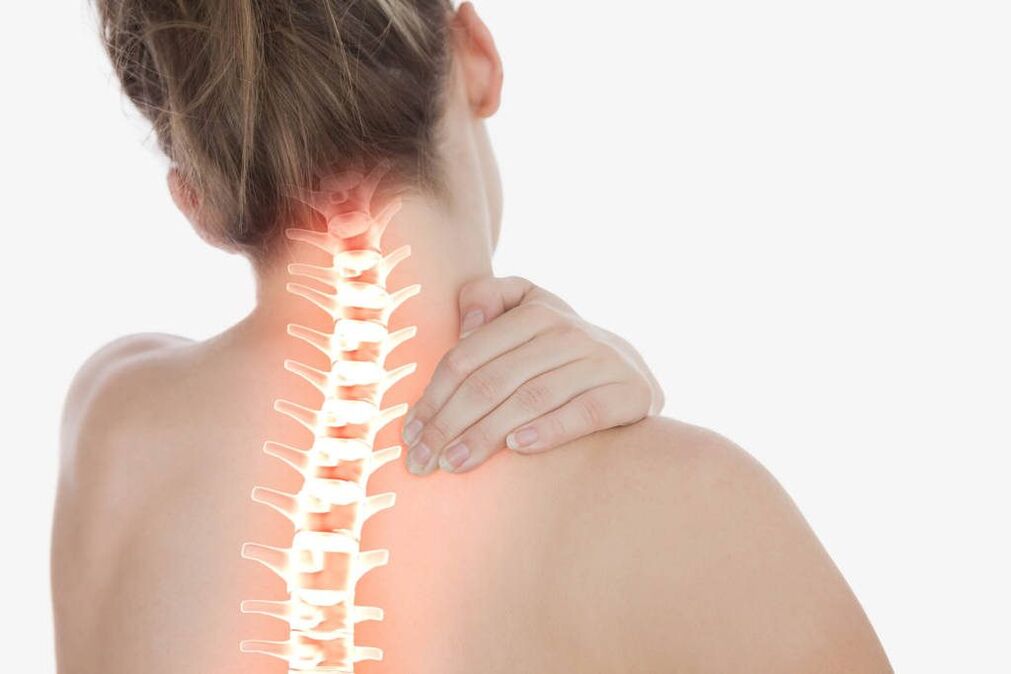
In cervical osteochondrosis, dizziness and painful sensations may occur when the head is turned. The onset of the first painful sensations is observed in the back of the head and is similar to the head. Inflammation of cartilage to nerve fibers, causing vasospasm.
Chest osteochondrosis
The development of thoracic osteochondrosis can be masked for a long time as a cardiovascular disease. Typical symptoms:
- violation of tactile sensations and numbness of the limbs;
- tingling in the intercostal space;
- pain in the heart area, arrhythmias;
- restriction of respiratory functions, difficulty in the sternum;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract (inflammation of the pancreas, bloating);
- radiates pain to the shoulder blade region.
Lumbar osteochondrosis
Progressive lumbar osteochondrosis in advanced form can lead to disability. The inflamed area of the spine stops the supply of trace elements to the lower extremities for full joint and muscle function. The pinched cells of the nerve trunk cause unbearable back pain and medication.
The main symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis are:
- numbness of the lower extremities;
- sore muscles, weakness;
- chills;
- muscle cramps;
- dysfunction of the reproductive system;
- the pain may be sharp or aching in the lumbar region, radiating towards the foot.

Diagnostics
On average, there are 20 inhabitants diagnosed with osteochondrosis per 1, 000 inhabitants. Diseases such as osteochondrosis are difficult to diagnose at an early stage. His symptoms are quite hidden and obviously only appear in 2-3 stages when it comes time for serious medication.
If the development of osteochondrosis is suspected, a specialist should be consulted first and a comprehensive examination should be performed to clarify the differential diagnosis and diagnosis.
Doctors use three standard diagnostic methods:
- Neurological.
- Instrumental.
- Laboratory.
The primary neurological examination of the patient is performed by a neurologist, determining the category of nerve structures affected by the disease. Furthermore, in order to exclude different types of diseases with similar symptoms, the patient may be referred for X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, and ECG examination.
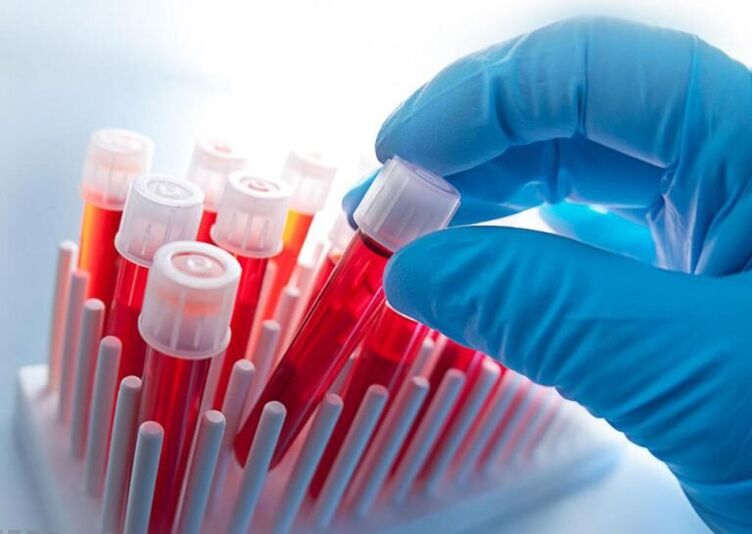
Laboratory (analyzes)
Laboratory diagnostics is advisory - auxiliary. Blood tests show an increase in the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation and a decrease in calcium levels. This means the course of pathological processes in the body, but does not indicate the peculiarities of their development. Therefore, this method is included in the comprehensive examination of the patient and its results are deciphered based on other medical data.
Instrumental
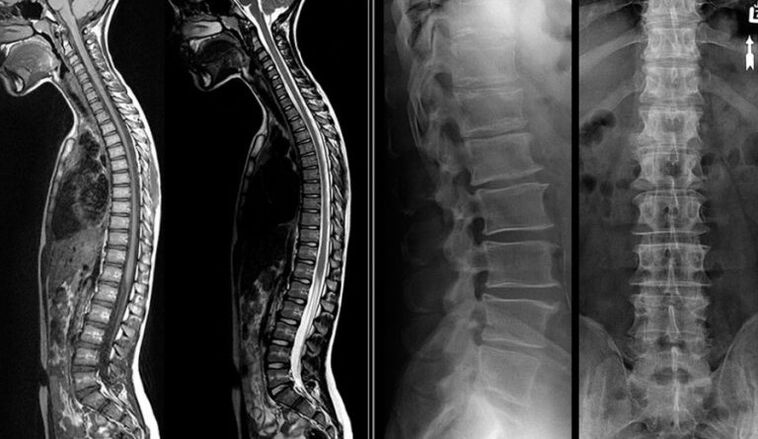
Diagnostics using professional equipment provides the most accurate results for a variety of diseases. The main research tools are:
- X - ray reveals anatomical changes in bones, cartilage, nerve tissue.
- MRI - magnetic resonance imaging. It allows the visualization of processes taking place in bone and soft tissues, blood vessels and nerve fibers.
- CT (computed tomography) - similar to MRI, but produces radiation.
- Electromyography - can decipher neurological symptoms.
Traditional treatment
The treatment regimen for osteochondrosis is traditional. Ingredients of drug therapy in different directions: NSAIDs, chondroprotectors, analgesics, hormonal agents and supporting vitamin complexes. In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapy, manual therapy, reflexology, surgery, massage, and preventative measures are used to combat osteochondrosis.

Drug therapy
Back pain due to osteochondrosis is immediately impossible to stop forever, but pharmacological drug therapy gives breath to the lower back. Strong anesthetics and anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have an analgesic effect and trigger the fight against inflammation in the spinal regions. Essential medications for the treatment of osteochondrosis of the back:
- Chondroprotectors are drugs that restore cartilage tissue elasticity and vertebral mobility.
- Muscle relaxants - soothing cramps in muscle structure.
- Vascular system - improves blood circulation and metabolic processes.
- Vitamin complexes and antioxidants.
Only with the use of a properly selected therapeutic complex can positive dynamics be achieved and the result be maintained for a long time.
Different medicines are used to treat osteochondrosis of the back:
- External remedies: ointments, creams, gels.
- Preparations for internal consumption: capsules, tablets.
- Medication injections.
Surgical intervention
Unfortunately, there are cases of osteochondrosis where treatment time is missed and medications do not give the expected results and the disease progresses. Then the only solution is surgery. The main reasons for this operation are:
- Removal of the intervertebral hernia that compresses the spinal cord.
- Reduction of intervertebral crack to 1/3 of original size.
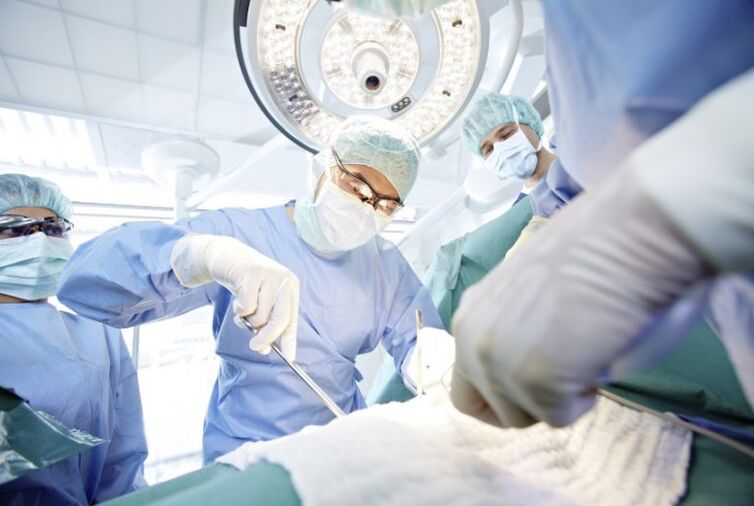
The referral for surgery may be prescribed by the physician based on the patient's complete diagnostic picture and the existence of direct indications for the removal of the pathological defect. In spinal surgery, the leading position is taken by the discectomy method - surgical removal of the disc by deformation. The devices can be microdiscectomy, B-Twin system or laser evaporation of the core. Rehabilitation after spinal surgery lasts for six months.
Gymnastics
Gymnastics or exercise therapy is an excellent supportive therapy for the treatment of osteochondrosis. Regular exercise helps to:
- Strengthen the muscle corset - this is necessary for an even load on the spine.
- Stimulation of blood circulation to saturate bone and muscle tissue.
- Develop the correct posture.
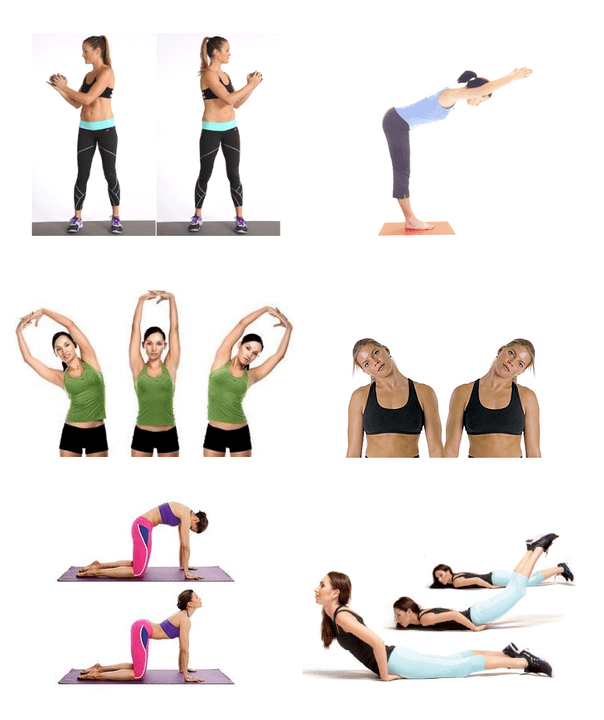

It is important to note that practices should be tailored to the diagnosis and should adhere to the following principles:
- Regularity of implementation.
- Smooth movement, no jerks.
- In case of painful feelings, the load should be reduced or the exercise should be stopped.
- Watch your well-being.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is indicated for patients with osteochondrosis of the back to relieve inflammation and is performed in places where the disease is concentrated. Treatment courses contribute to:
- Increasing body resistance.
- Restoration of metabolism in the affected sector.
- Relieve pain and swelling.
- Improving vascular circulation.
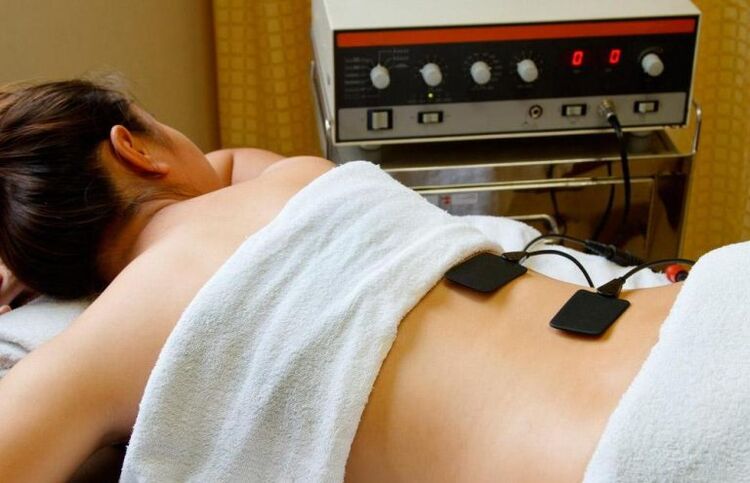
To select a physiotherapy method for the treatment of osteochondrosis, the desired result must be clearly defined. Mainly used:
- Laser therapy.
- Ultrasound exposure.
- Electrical stimulation.
- Magnetotherapy.
Diet
There is no single diet for patients with osteochondrosis. However, physicians unanimously agreed that the use of the following categories of products with this diagnosis is categorically not recommended:
- Fatty broth soups.
- Pork and other fatty meats.
- Animal fats of birds (geese, ducks).
- Coffee, caffeinated spirits.
In addition, alcohol and sweets are limited on the menu.
For example, you can use diet 15 on a diet. It contains all the vital macronutrients, minerals, vitamins and carbohydrates. The energy value of the right menu is 2600-2700 kcal, i. e. 85-90 g of protein, 350-400 g of carbohydrates and 90-95 g of fat.
Thus, the ideal menu for a patient with osteochondrosis is a combination of balanced, non-nutritious foods rich in vitamins and minerals. Meals are divided into small portions 6 times.
Traditional treatment
Folk remedies are often used at home to relieve inflammation, relieve pain and muscle cramps, and strengthen the body in general. There are many recipes for decoctions and infusions of traditional medicine that are used in three main ways:
- rubbing;
- compresses;
- herbal baths.
Daily use allows you to get rid of the discomfort in 10-14 days. Traditionally, folk remedies can be divided into systemic and local effects on the body.
System tools
You can use natural systemic preparations in the form of decoctions to affect the whole body and spine.
An example of a positive effect is the effect of yarrow decoction, which relieves pain, fights inflammation and soothes.
Local funds
Topical remedies for folk remedies include ointments, infusions for compressing and rubbing. These foundations should be mixed according to the recipe and applied to the inflamed area, but only if there is no allergy to the ingredients and skin damage. Among the popular compositions, special attention is paid to honey compresses, ginger ointment in the tincture of marigold pharmacy, a mixture of plantain and sage herbs, rubbed with horseradish with vodka.
You should consult your doctor to select an effective method and prescription, as home treatment methods are only an integral part of general therapy and have only an additive effect.
Prophylaxis
Therapeutic therapy for back disease cannot be achieved without measures to prevent long-term success. Even the most effective and expensive medicine does not guarantee a return of symptoms due to a return to daily stress in the body. Therefore, the positive effect should be consolidated and maintained by applying a few simple rules:
- Do not lift weights over 10 kg.
- Observe the even distribution of the load on the back muscles.
- Pay attention to rationality and balance in nutrition.
- Take restorative vitamins and active supplements (mucopolysaccharides).
- Develop a system for rest and work change.
- Maintains physical activity.
Keep in mind that this category of disease is latent in nature. Therefore, osteochondrosis of the back should not be allowed at the time of diagnosis, even in the absence of obvious symptoms. Adherence to all of your doctor’s recommendations and home care will allow you to return to normal functioning more quickly after treatment, but continuous monitoring is needed to prevent it from getting worse.


























